
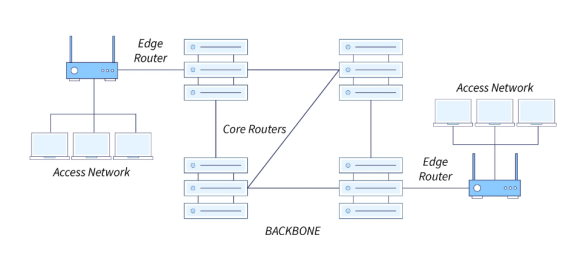
The Access Network is a network that connects the final system to the direct router (also known as the “edge router”) from the end system to any other remote system. Examples to access networks are ISP, family network, corporate network, ADSL, mobile network, ftth, etc.
Types of access networks(Featured):
Ethernet - It is the most common wired LAN technology that provides services on the Physical and Data Link layer of the OSI reference model. Ethernet LAN usually uses coaxial cables or distorted pairs.
DSL - DSL represents a Digital Subscriber Line, which brings the connection to your house through a telephone line. The DSL line can carry both data and voice signals, and the data part of the line is continuously connected. In DSL, you can use the Internet and make phone calls simultaneously. DSL modems use telephone lines to exchange data with digital subscriber line access multiplexers (DSLAMS). In DSL, we obtain 24 Mbps and 2.5 Mbps downstream.
FTTH - Fiber to the home (FTTH) directly uses the fiber of the central office (CO) for individual buildings and provides high-speed internet access between all access networks. It ensures a high initial investment, but the future investment is relatively small, which is the most expensive and suitable choice among all these access networks for the future.
Wireless LANs - It uses wireless communication to link two or more devices within the range. It uses high -frequency radio waves, usually includes access points connected to the Internet.
3G and LTE - It uses a cell phone to send or receive data packets through a nearby base station operated by a honeycomb network provider. The term "3G Internet" refers to the third -generation mobile phone standard set by the International Telecommunications Alliance (ITU). Long -term evolution (LTE) provides high -speed wireless communication for mobile devices and increases network capacity.
Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) - HFC is a combination of fiber and coaxial cables. Wired TV operators are widely used to provide high -speed Internet access. Optical fiber cables are used to connect the head end to the neighborhood, and use coaxial cables to connect a single house to the network.
Satellite Internet - Satellite Internet is a wireless connection that uses satellite communication to visit the Internet access remote control area and rural areas. Compared with other access networks, it has higher latency and lower bandwidth, but it can provide Internet access in areas available in other options.
Power Line Communication (PLC) - PLC uses the existing wires in the building to transmit data signals. It is a low -cost alternative to the traditional wired network, which can be used to provide Internet access in buildings that are difficult to install new cables.
WIMAX -WIMAX (global interoperability fof Microwave Access) is a wireless access network technology that provides high -speed Internet access in a wide area. It is usually used to deploy cable network difficulties or expensive rural and suburbs.
5G - 5G is the latest wireless communication technology that can provide high -speed Internet access and increase network capacity. It aims to support extensive applications, including virtual and augmented reality, autonomous cars and smart cities. The 5G network is being launched worldwide, and it is expected to change our way to connect to the Internet.
What Does an Access Network Do?
FTTH
· Install and use the optical fiber from the center position, directly to a single structure, such as houses, apartment buildings and enterprises with high -speed Internet access, called house (FTTH), sometimes called fiber (sometimes called fiber) (FTTP). In terms of connection speed provided to computer users, most regions have improved technology.
· FTTH (Mbps) promises that the connection speed per second is up to 100 mega. Compared with the standard cable modem or DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), these speeds are 20 to 100 times. Because it needs to install a new cable set from the existing fiber cable to the "last link" of a single user, it is expensive to realize FTTH in the large scale.
Benefits of FTTH
· The key advantages of FTTH improve the network performance, especially faster. The longer speed is to use coaxial cables, distorted pairing conductors and more traditional technologies that cannot be provided by DSL.
· Experts believe that due to its significant increase in bandwidth, FTTH is the biggest technology to solve consumer network demand in the next decades. The advantages of this include:
1. The performance of high -definition video streams is enhanced on platforms such as YouTube and Roku.
2. Some people call FTTH "future proof" because it can upgrade multiple times without changing fiber. It can update the fiber support infrastructure without affecting the fiber itself.
3. The greater distance is more than the speed than early technology. It is better than other fiber design, because the fiber can be directly linked to the house, and it can be used to complete the remaining network segment to complete the surplus network segment.
Why Is GPON Popular in FTTH Network?
GPON (Gigabit passive optical network) is defined by the ITU-T recommended series G.984.X. It can not only transport Ethernet, but also transport ATM and TDM (PSTN, ISDN, E1 and E3) traffic. Compared with ATM PON (APON) and Broadband Pon (BPON), it indicates an increase in bandwidth. In many schemes, especially in the FTTX network, three games can be applied, high bandwidth and long distance (20KM long) high (up to 20 kilometers). In addition, GPON customers are usually houses or small companies. Because GPON technology can convey data, voice and IP videos, it is suitable for fiber for fiber -to -home (FTTH) transmission. In the FTTH application, the FTTH network based on the passive optical network (PON) is a point -to -point fiber, that is, the optical fiber of the housing network architecture. In this architecture, an unpowered optical split device is used to enable a single optical fiber to use it to use it to use it to use it to use a single optical fiber to use it to use it to use it. The premise of service 32-128. The following texts will focus on the components and architectures of GPON FTTH access to the network.
Components of GPON FTTH Access Network
In the GPON FTTH access network, there are three main components: light terminal (OLT), optical separator and optical network terminal (ONT).
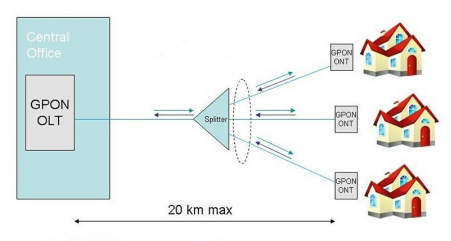
Architecture of GPON FTTH Network
Through the tree topology, GPON uses the minimum network to maximize the coverage of the light, thereby reducing the light function. The FTTH access network includes five areas. They are core network areas, central office areas, feedback areas, and allocated areas and user areas/customer places (see the figure below).
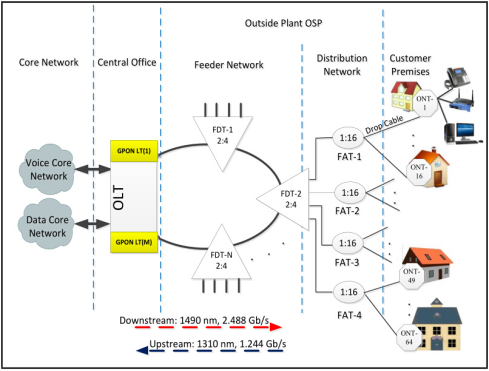
Core Network
The core network includes ISP devices of Internet service providers, PSTN (Public Switch Telephone Network, data packet switch or traditional circuit switch) and cable TV provider equipment.
Central Office
The main function of the central office is to host OLT and ODF (Optical Distribution Framework) and provide necessary motivation. Sometimes it may even include certain components of the core network.
Feeder Network
The feed line is extended from ODF from the Central Office (CO) to the distribution point. These points (usually street cabinets) are called Fiber Distribution Terminals (FDT), of which 1 level division division is usually located in it. The feed cable usually starts as a ring -colored connection from the GPON port and terminates another GPON port, as shown in the figure above to provide type B protection.
Distribution Network
The Level-1 separator of the distribution cable is assigned to use the level 2 assignor (within the FDT). Class 2 separators are usually hosted in a box installed in a rod. It is called a fiber connection terminal (fat), and is usually placed at the nearby entrance.
User Area
In the user area, the drip cable is used to connect the two-stage separator inside the fat to the subscriber premises. For ease of maintenance, the aviation drop cable is usually terminated at the entrance of the user's house using a terminal box (TB), and then the indoor dropped cable connects the TB to the access terminal box (ATB) inside the house. Finally, the patch cable connects the ONT to the ATB.
Conclusion
From all the above, GPON technology plays an important role in the FTTH network. GPON -based FTTH network architecture is reliable, scalable and secure. Since it is a passive network, from CO to end users without activity components, this will greatly reduce network maintenance costs and requirements. GPON -based FTTH is a future solution to provide broadband services.





 INQUIRY
INQUIRY